By Mrs. Ayesha
What is ASD? What should parents know about it?
Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by various difficulties in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. The term “spectrum” reflects that each person with autism has a wide range of challenges and strengths. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 1 in 54 children in the United States are affected by ASD, making it a prevalent condition that requires awareness and understanding.
ASD affects how a person communicates, interacts with others, and experiences the world. Here is a simple explanation for parents:
# What is ASD?
1. **Differences in Communication:** Children with ASD may have trouble speaking or understanding language. They might not respond to their name or find it difficult to express their needs with words.
2. **Social Interaction Challenges:** They might avoid eye contact, find it hard to play with other children, or prefer to be alone. Understanding social cues like facial expressions and tone of voice can be challenging for them.
3. **Repetitive Behaviors:** Children with ASD often engage in repetitive actions, such as rocking back and forth, flapping hands, or repeating the same words over and over. They may have a deep interest in specific topics.
4. **Sensitivity to Sensory Input:** They may be very sensitive to sounds, lights, textures, or other sensory inputs. For example, loud noises or bright lights might be overwhelming for them.
# Things to Keep in Mind:
1. **Each Child is Unique:** ASD affects each child differently. Some may need a lot of support, while others may need less.
2. **Early Intervention Helps:** Getting support early, such as speech therapy or special educational programs, can make a significant difference in helping a child with ASD develop their abilities.
3. **Strengths and Talents:** Children with ASD often have unique strengths and talents. Focusing on these can help them thrive and grow.
Understanding ASD is the first step to providing the right support and care, enabling a child to reach their full potential.
#Symptoms and Diagnosis
ASD typically appears in early childhood, often before the age of three, and can affect a person throughout their life. Common symptoms include:
1. **Social Challenges:** Difficulty understanding social cues, forming relationships, and engaging in typical social interactions.

2. **Communication Difficulties:** Delayed speech development, unusual speech patterns, or difficulty understanding and using language.

3. **Repetitive Behaviors:** Repeating certain actions or behaviors, such as hand-flapping, rocking, or insisting on routines. A comprehensive evaluation by a multidisciplinary team, including pediatricians, psychologists, and speech therapists, is required to diagnose ASD. The evaluation typically includes observing the child’s behavior, interviewing parents, and using standardized tests.

# Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of ASD is unknown, but research suggests a combination of genetic and environmental factors may play a role. Some identified risk factors include:
1. **Genetic Influences:** Certain genetic mutations and conditions, such as Fragile X syndrome, are associated with ASD.
2. **Environmental Factors:** Prenatal exposure to certain medications, complications during pregnancy, and advanced parental age are linked to an increased risk of ASD.
3. **Biological Factors:** Differences in brain structure and function have been observed in individuals with ASD.
# Interventions and Support
While there is no cure for ASD, early intervention and tailored support can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with autism. Common interventions include:
1. **Behavior Therapy:** Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a widely used approach focusing on improving specific behaviors through positive reinforcement.
2. **Speech and Language Therapy:** Helps individuals develop effective communication skills, whether through speech, sign language, or alternative communication devices.
3. **Occupational Therapy:** Aims to enhance daily living skills and sensory processing abilities.
4. **Educational Support:** Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) ensure that children with ASD receive appropriate accommodations and support in school settings.
# Living with ASD
With the right support and understanding, individuals with ASD can lead fulfilling lives. Many people with autism possess unique strengths, such as exceptional attention to detail, strong memory skills, and creativity. It is important to recognize and celebrate these strengths while providing the necessary resources to address challenges.
Families and caregivers play a crucial role in supporting individuals with ASD. Joining support groups, accessing community resources, and seeking professional guidance can help families navigate the complexities of autism.
# Promoting Awareness and Acceptance
Raising awareness and acceptance of ASD is essential for creating an inclusive society. Misunderstandings and stigma around autism can lead to isolation and discrimination. By promoting understanding and empathy, we can create a more inclusive environment where individuals with ASD can thrive.

#Activities for Children with ASD:
**Speech and Language Therapy:**
– Helps children with pronunciation and understanding words.
– Uses pictures and signs to improve communication skills.

**Social Skills Training:**
– Helps recognize and use social cues correctly.
– Games and group activities with peers.

**Behavior Therapy (Applied Behavior Analysis – ABA):**
– Improves specific behaviors through positive reinforcement.
– Helps manage challenging behaviors.

**Occupational Therapy:**
– Improves motor skills and sensory processing.
– Teaches everyday activities like writing, buttoning, and bathing.

**Physical Activities and Sports:
– Helps manage energy and promotes social interaction.
– Group games, running, swimming, and yoga.

**Music and Art Therapy:**
– Reduces sensory stimulation and improves communication.
– Singing, playing instruments, and painting.

*Visual Schedules and Plans:
– Provides clear structure and routine for daily activities.
– Helps plan activities and manage time.

Sensory Breaks:
– Provides relaxation time to avoid excessive sensory stimulation.
– Quiet and safe spaces.

Mindfulness and Meditation:
– Reduces stress and anxiety.
– Simple meditation techniques and deep breathing.

**Social Stories and Role-Play:**
– Helps understand and prepare for social situations.
– Practice different social scenarios.

These activities help children cope with ASD and aid in their development. It is always important to consult a professional to create an appropriate and effective treatment plan.
# Conclusion
Autism Spectrum Disorder is a multifaceted condition that affects individuals differently. Through early diagnosis, individualized interventions, and social acceptance, individuals with ASD can reach their full potential. As a community, it is our responsibility to support and uplift individuals with autism, ensuring they have the opportunity to lead meaningful and fulfilling lives.
For more information and resources, please visit organizations such as Autism Speaks, the Autism Society, and the CDC’s ASD page.
# Do’s and Don’ts for Supporting Individuals with ASD
Do:
– Provide Consistency and Structure:Create a predictable routine and maintain it as much as possible. Use visual schedules and timers to help individuals understand what to expect.
–Use Clear and Direct Communication: Use simple, straightforward language. Be clear about your expectations and instructions. Use visual aids and gestures to support verbal communication.

Encourage Social Interaction:** Provide opportunities for social interaction in controlled and supportive environments. Encourage participation in social skills groups or activities with peers.

Focus on Strengths and Interests:** Identify and encourage activities that align with the individual’s interests and strengths. Use these interests as motivation for learning and engagement.

Be Patient and Understanding:** Allow them to communicate in their own ways and at their own pace.

Provide Positive Reinforcement:** Praise and reward positive behaviors and efforts. Use a reinforcement system that is meaningful to the individual.

Create Sensory-Friendly Environments:** Be mindful of sensory sensitivities and make adjustments as needed. Provide a quiet space for relaxation and sensory breaks.

Educate Yourself and Others:** Learn about ASD and the specific needs of the individual you are supporting. Educate family members, friends, and peers about autism to promote understanding and acceptance.
Collaborate with Professionals:** Work with therapists, teachers, and healthcare providers to develop and implement effective support strategies. Follow recommended interventions and therapies.

Don’t:
Overwhelm with Too Much Information:** Avoid giving multiple instructions at once. Break tasks into small, manageable steps.
Assume All Behaviors Are Intentional:** Understand that some behaviors may result from sensory overload, anxiety, or difficulty communicating needs. Avoid punishing behaviors that are manifestations of their condition.

Force Eye Contact:** While eye contact is a social norm, forcing it can cause discomfort and anxiety. Encourage eye contact gently and accept other forms of engagement.

Use Sarcasm or Abstract Language:** Individuals with ASD may have difficulty understanding sarcasm, idioms, and abstract concepts. Use clear, literal language.
Ignore Sensory Needs:** Be aware of sensory sensitivities and avoid environments that may cause distress. Provide sensory tools and breaks as needed.

Change Routines Abruptly:** Avoid sudden changes in routines without warning. Prepare individuals in advance for changes and provide clear explanations.

Underestimate Abilities:** Recognize and support the capabilities and potential of individuals with ASD. Provide opportunities for them to showcase their skills and talents.

Be Inflexible:** While consistency is important, be flexible in accommodating the individual’s needs and preferences. Adapt strategies as needed to find what works best.
Isolate or Exclude:** Ensure that individuals with ASD are included in activities and social interactions. Create an inclusive environment where they feel valued and accepted.

By following these do’s and don’ts, you can create a supportive and understanding environment for individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder, helping them thrive and reach their full potential.
**Home Activities for Children with ASD Under Parental Supervision:**
**Speech and Language Exercises:**
– **Use of Flashcards:** Use picture and word cards to promote vocabulary and recognition.


– **Reading Stories:** Read books with children and ask them questions.


**Social Skills Development:**
– **Role-Play:** Act out various social scenarios, such as making friends or attending a birthday party.
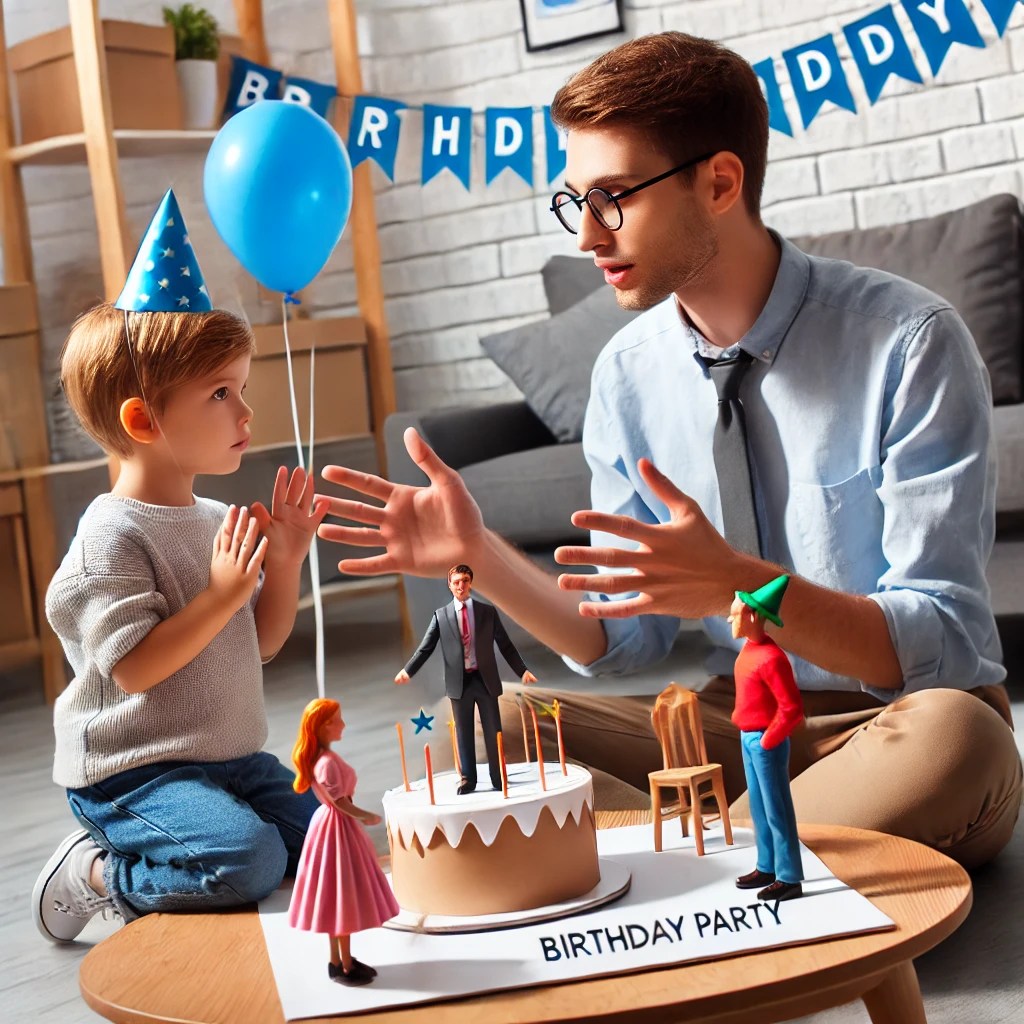


– **Family Games:** Practice social interaction through family games.
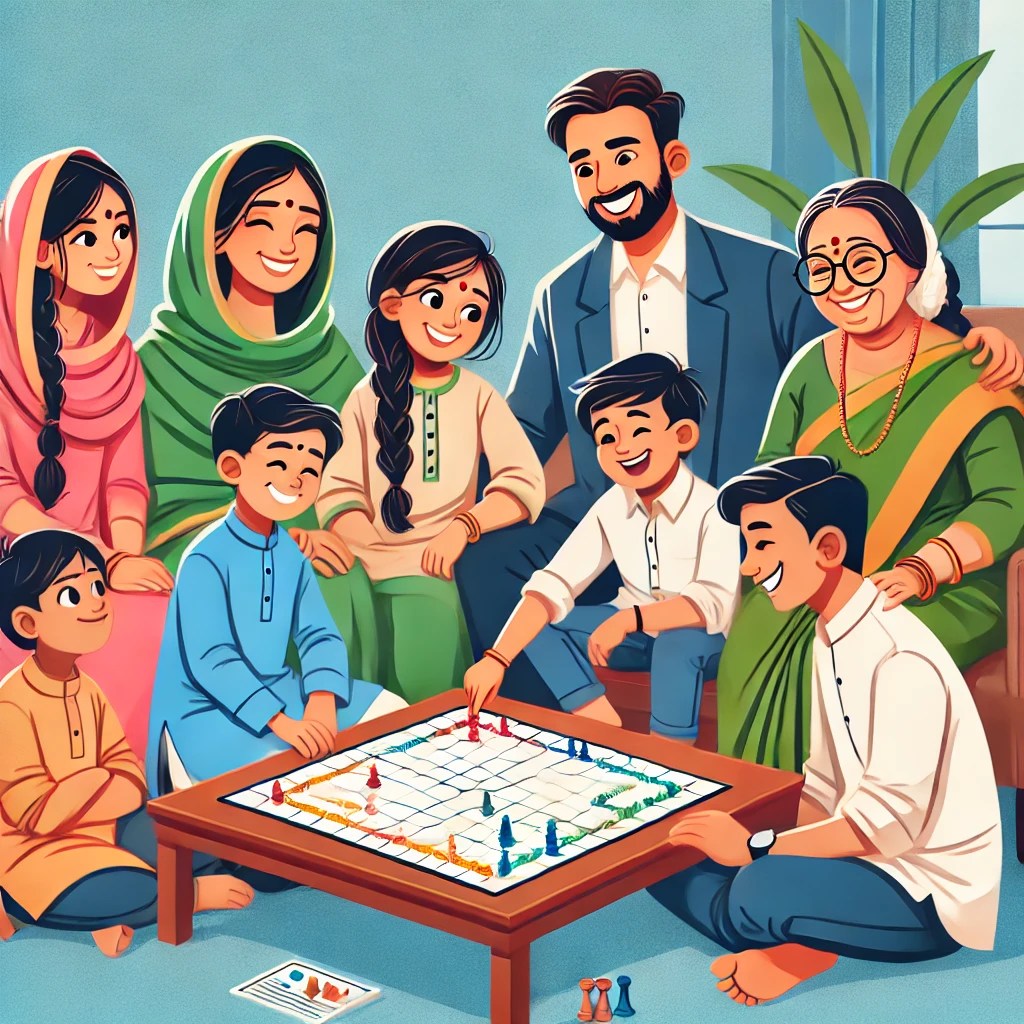
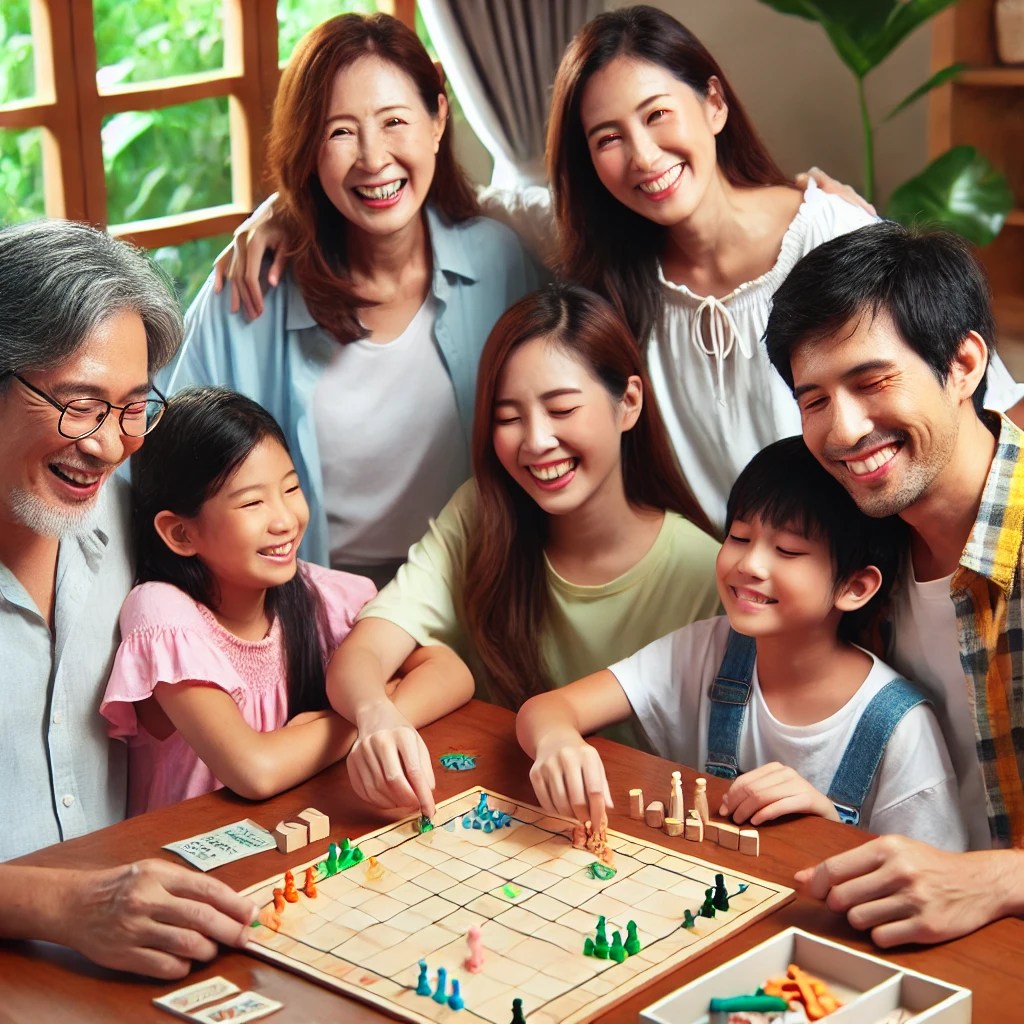


**Sensory Activities:**
– **Sensory Bins:** Allow play with containers filled with various textured materials (e.g., rice, beans, water beads).
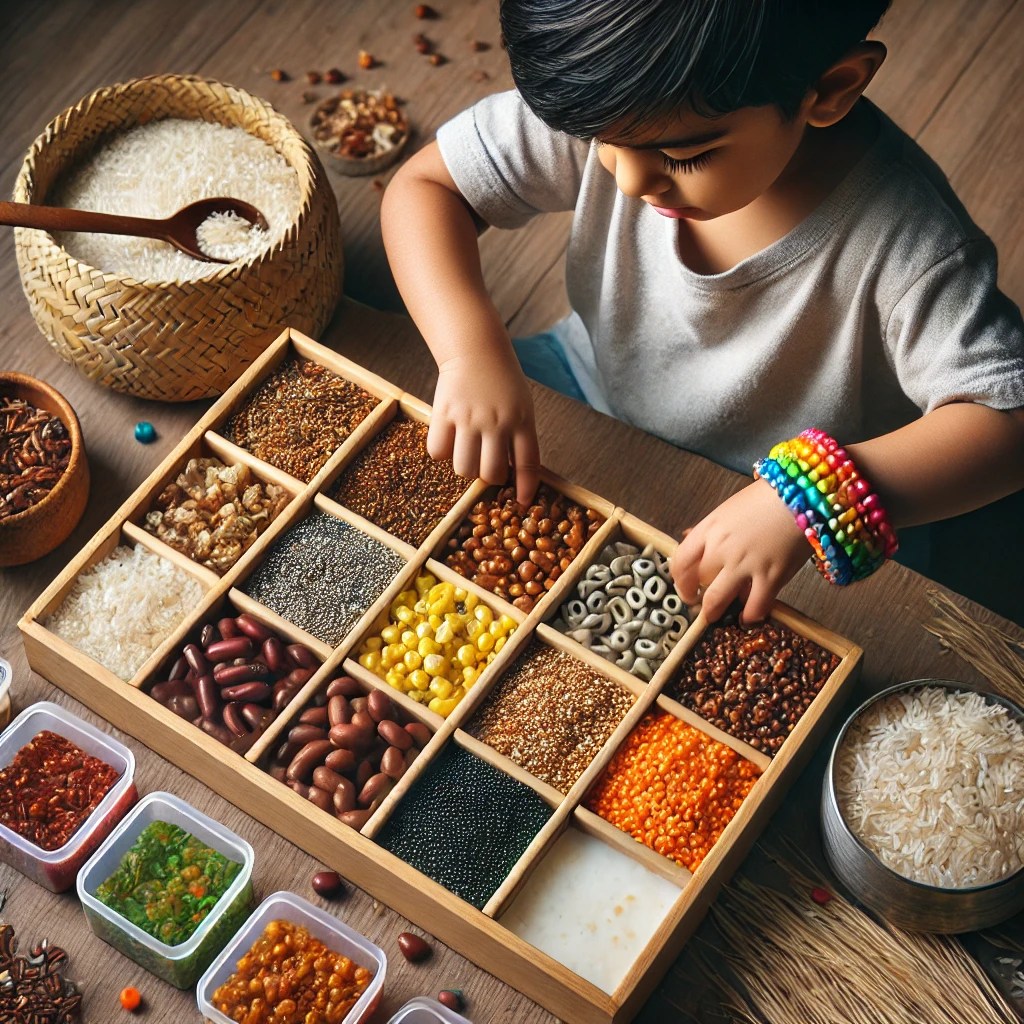


– **Swing or Trampoline:** Use swings or trampolines for balance and sensory input.


**Motor Skills Practice:**
– **LEGO or Blocks:** Play with LEGO or blocks to develop fine motor skills.


– **Drawing and Painting:** Improve hand-eye coordination through art and craft activities.


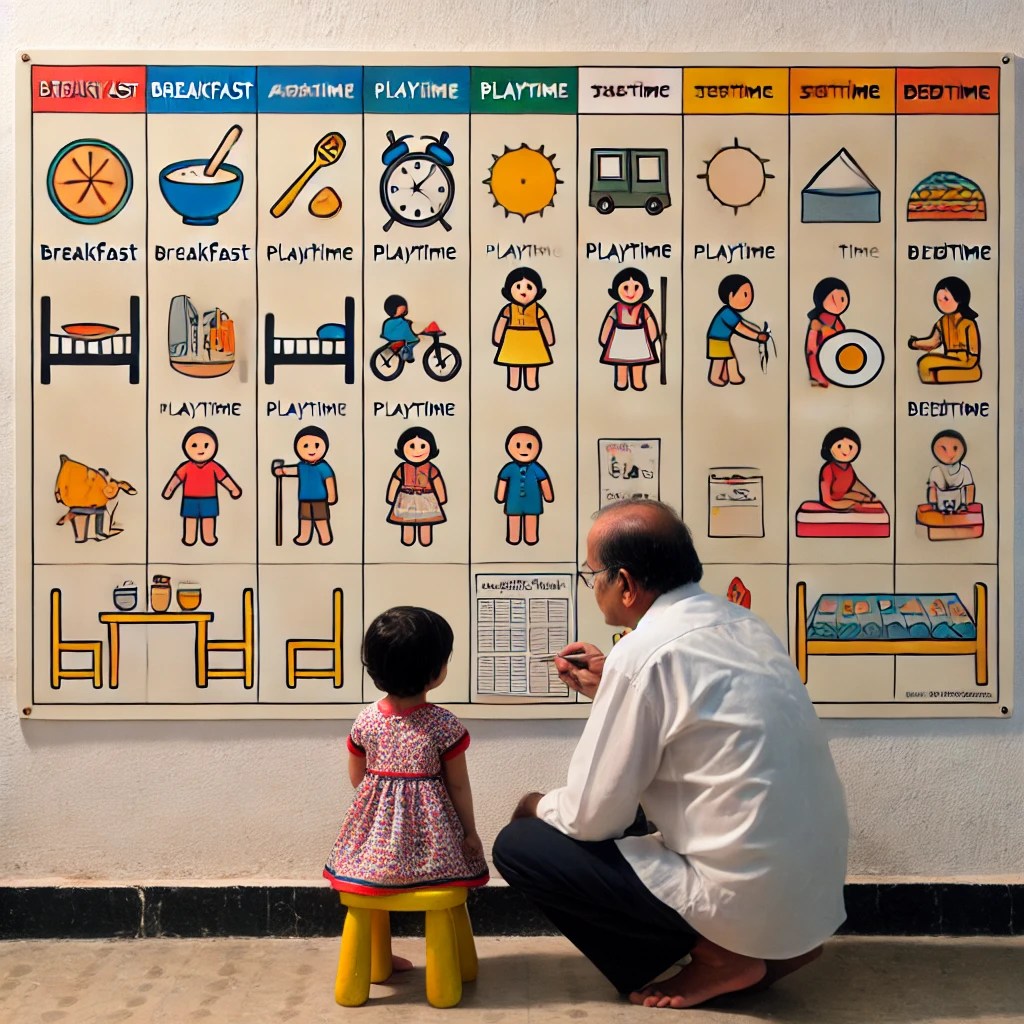
**Routine and Structure:**
Visual Schedule:** Create a visual schedule for daily activities to help the child understand routines.


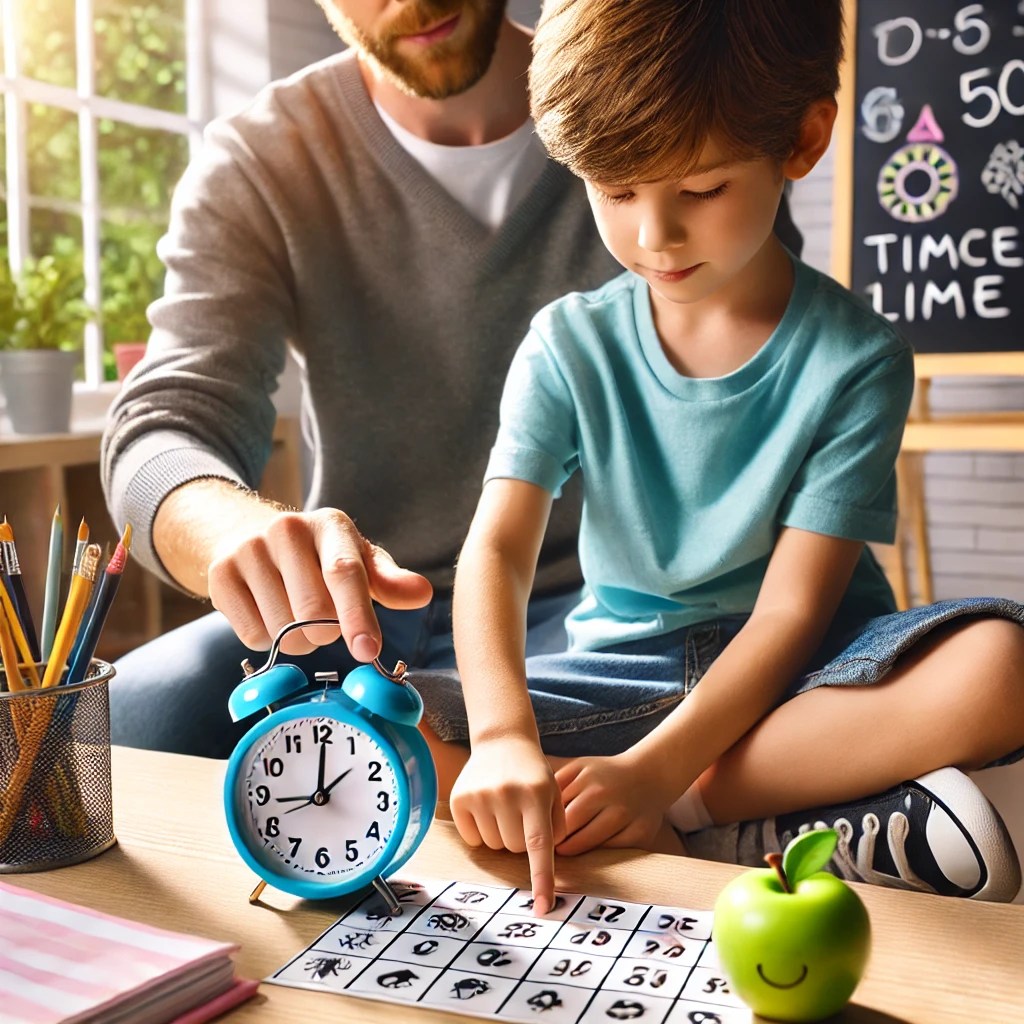
– **Use of Timer:** Use a timer to set time limits for activities.


**Music and Dance:**
– **Listening and Singing:** Sing and dance to favorite songs.
– **Playing Instruments:** Use simple instruments like tabla, harmonium, or cymbals.
**Physical Activities:**
– **Yoga and Stretching:** Practice simple yoga poses for children.
– **Mini-Workout:** Engage in small workouts or games like running, jumping, and skipping.
**Puzzles and Games:**
– **Jigsaw Puzzles:** Promote problem-solving and concentration.
– **Board Games:** Develop social skills and strategic thinking.
**Social Stories and Videos:**
– **Social Stories:** Read social stories written specifically for ASD children.
– **Educational Videos:** Show educational videos that promote communication and social skills.
**Mindfulness and Meditation:**
– **Deep Breathing Exercises:** Practice simple meditation techniques and deep breathing.
– **Mindfulness Games:** Play games that promote mindfulness.
Parents can regularly and patiently include these activities in the child’s routine. It is important to choose activities considering the needs and abilities of each child.



